NIST data demonstrates INNOTYPER 21 utility for degraded samples
January 6, 2017
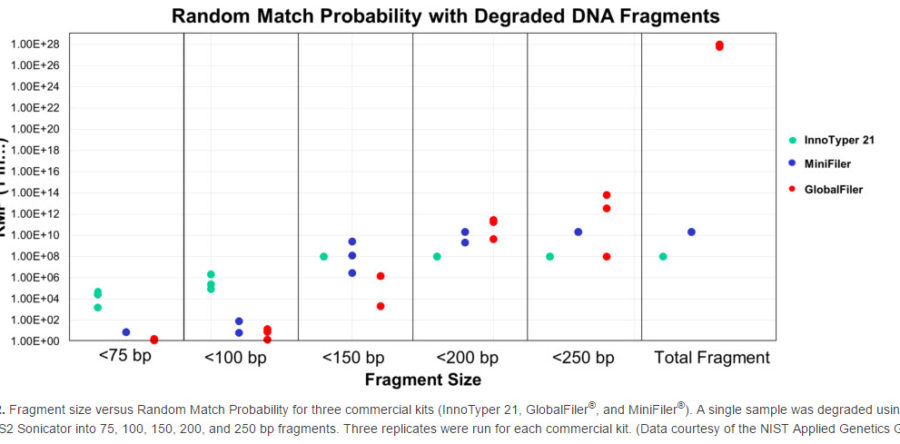
In studies conducted by the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) Applied Genetics Group, the InnoTyper 21 kit proved to be more discriminating than traditional STR and mini-STR multiplexes for degraded DNA fragments less than 150 base pairs in size. The studies, which were presented in a recent AAFS poster (click here to view), included analysis of 660 samples from 3 major U.S. population groups (African American, Caucasian, Hispanic) to generate allele frequencies and population genetic parameters. A sample was then degraded into multiple, fixed fragment lengths and each length amplified in triplicate with InnoTyper 21, GlobalFiler and MiniFiler kits for comparison of allele recovery and random match probabilities. Several kinship scenarios were also tested including samples with simulated degradation. In addition to the work presented in the poster, further research was conducted by NIST to confirm the lack of significant genetic association between the INNUL markers in InnoTyper 21 and commonly used forensic STR markers. This research, which supports the ability to combine random match probabilities generated by STR kits and InnoTyper 21, will be included in a forthcoming journal article.

